INTRODUCTION
The MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery) program is an undergraduate program open to local students who obtain the highest marks in the science stream at the Advanced level examination. Admissions are done under the University Grants Commission based on the district vice merit order.
International students are also admitted to this program through government sponsored schemes. Currently Bhutanese and Maldivian students are admitted.
Curriculum
Background
Despite been nearly 50 years old, the Faculty of Medicine (FoM), University of Peradeniya (UoP) has an evolving and dynamic curriculum. In 2002 an attempt was made to create an integrated curriculum. Around the same time many faculties within the University system in Sri Lanka changed over from the British 3 Term, subject based curriculum with class based examination outcomes to the American two semester module based, credit valued curriculum ending with a GPA.
Current State
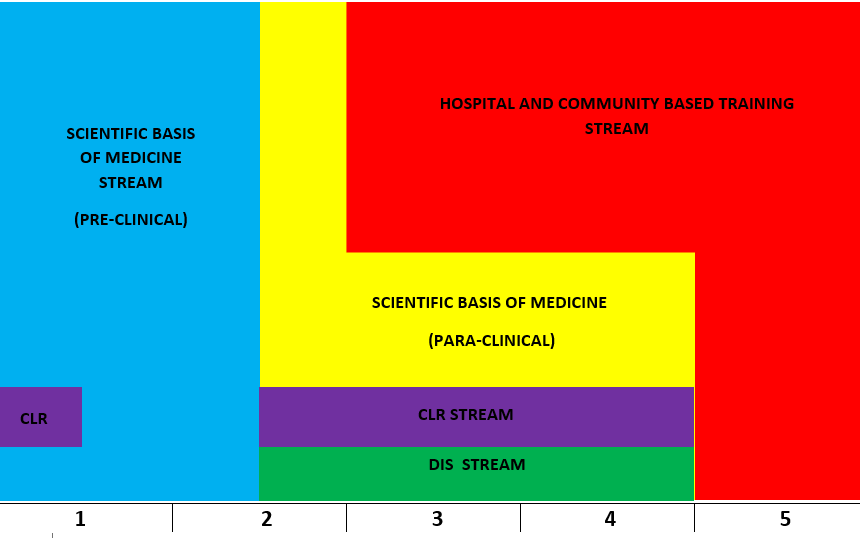
The FoM at Peradeniy now has a 5-year undergraduate curriculum for the Degree of MBBS, which can be broadly divided into two parts;
- An integrated module based, credit valued non clinical part, starting in year one and ending at the end of year four. This is organized under the following streams;
- CLM - Clinical, Laboratory and (patient) Management skills (Y1 and 2 at tandem with SBM)
- SBM- Scientific Basis of Medicine - providing the knowledge base for the above skills
- CLR - Communication and English, Learning (including web based), and Research skills
- DIS - Doctor In Society - Population issues and justice through Medicine
- HCT - Hospital and Community based Training (minimally in first two years)
- The clinical curriculum which starts at the beginning of year 3 and finishes with a summative examination called the Final MBBS at the end of the 5th year. A large part of this examination is common to all medical faculties in the country. This enables a National Merit Order List of Medical Graduates to be compiled.
It is obvious that the two parts of the curriculum run parallel during the 3rd and 4th years.
The Non-Clinical Part of the Curriculum
Human Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry, Growth, Development and Behavior together with Pathology, Infection Immunity, Pharmacology, the Community aspects of Medicine, Statistics, Research Methodology, Medical Jurisprudence, and medical ethics form the subject matter of this part of the curriculum. It is divided into 5 streams'-and taught in an integrated manner.
At the end of the Second Year (semester 4) a GPA is calculated for all work done up to that point. The GPA together with the results of the associated modular examination is called the 2nd MBBS examination. This forms a bar, which must be passed before entering clinical training.
A similar GPA is calculated for all the non-clinical work done in year 3 and 4 (Semester 5-8). This with the Results of the associated modular examination is called the 3rd MBSS examination and is called the year 4 examination.
The Clinical Curriculum
The Clinical Curriculum is, mostly hospital based training supplemented by lectures. It is intensive and involves long hours of work. General Medicine, Surgery, Paediatrics, Obstetrics Gynaecology and Psychiatry form the core of the training program. Clinical training and lectures are also carried out in Ophthalmology, Otolaryngology, Orthopedics, Urology, Gastroenterology, Medical and Surgical Cardiology, Neurology, Neurosurgery, Dermatology, Rheumatology, Pulmonary Medicine, Sexually transmitted Disease, Imaging, Anesthesia and Critical Care.
Hospitals used;
- National Hospital Kandy (2405 Beds)
- Teaching Hospital Pradeniya (960 beds)
- Sirimavo Bandaranayake Specialized Children Hospital
- Base Hospital (Teaching) Gampola
- District Hospital Nawalapitiya
The Final MBBS Examination is in 5 subjects, i.e. Medicine, Surgery, Obstetrics Gynaecology, Paediatrics and Psychiatry. The other areas are tested under the main subjects (Eg. Cardiology in Medicine)
The Faculty, the University and the UGC are in the process of developing a system for Credit allocation for clinical training in the Faculties of Medicine in Sri Lanka.
The entire course is taught in English.