Here the full thickness of the skin, subcutaneous tissues, muscle and/or the internal organs can get involve.
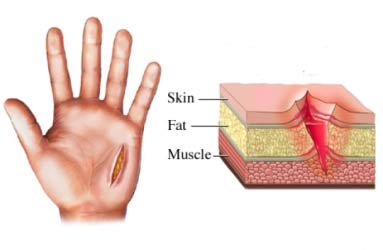
? Features of a laceration
Should observe the margins, ends, hair, hair bulbs and the floor
Types of lacerations
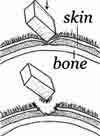
1. Split lacerations : caused by compression of the skin between the weapon & bone
e.g. a blow with a heavy blunt weapon on head, face, lateral & back of elbow, shin of the leg / hip
2. Torn lacerations : caused by a projecting surface of an object being dragged over the the skin
e.g. road traffic accidents , machinery accidents
3. Stretch lacerations : caused by a heavy blunt impact on a fixed, localized area of skin causing the skin to overstretch
e.g. machinery injuries
4. Perforated lacerations : caused by objects capable of penetrating the skin
e.g. missiles of firearms, shrapnel from explosions
5. Blast lacerations : caused by local blast effect of expanding gases
e.g. blast injuries
6. Cut lacerations : caused by blunted sharp weapons
e.g. ice picks, blade of a mammoty
7. Crush lacerations : occurs as a result of crush injury where the injury is caused by protruding bone fragments
e.g. crush injury of the head
8. De-gloved lacerations : caused by grinding force over the body resulting peeling off of the skin from underlying tissues
e.g. road traffic accident
Medico legal importance
- Gives a clue about the weapon used (but not the shape of the weapon)
- Indicates blunt trauma
- sometimes the shape of laceration gives a clue about the features of the weapon
- May indicate the point of impact of the weapon (e.g. split lacerations)
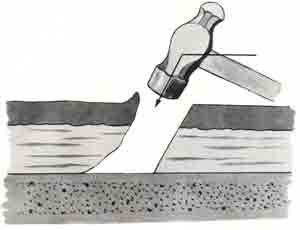 |
The arrow shows the direction of a impact . At the point of impact the skin splits cleanly and the torn skin is either everted or inverted. |
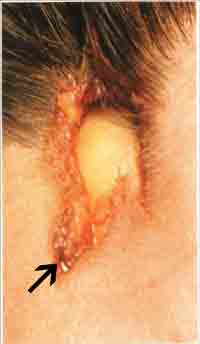 |
The arrow shows the rolled off edges with hair follicles everted. The point of impact is where the bone is seen. |
- A split laceration may mimic an incision
- It's important to differentiate antemortem lacerations from postmortem lacerations (e.g. animal bites )
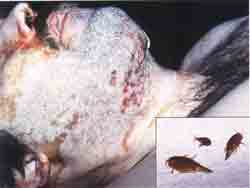
- Gives a clue about the mechanism of trauma and helps in reconstructing the incident - e.g. large area of skin rolled off caused by rotatory movements of tyres in Road traffic accident
- A laceration can be categorized for legal purposes
e.g. A laceration over the face results in a permanent scar which is grievous
lacerations of an internal organ may endanger life
- Useful in determining the time of injury / trauma
- Suggests the circumstances of injury e.g. homicide or accident. It is rarely seen in suicides and if found is most likely seen in psychiatric patients