|
|
||
|
A fracture is a
complete/incomplete
disruption of the continuity of bone. It
can result in either the complete separation or an incomplete crack.
|
||
 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
A fracture is a
complete/incomplete
disruption of the continuity of bone. It
can result in either the complete separation or an incomplete crack.
|
||
 |
|
|
|
Clinical features of a
fracture 1. Deformity - maybe visible and /or palpable 2. Local swelling, bruising, pain and tenderness 3. Impairment of function 4. Abnormal movements 5. Crepitations
|
Medico-legal importance
|
|
Simple fracture - closed fracture - no communication to the the outer environment
|
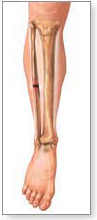
Bone has a single fracture and skin is intact. Complications are minimal
|
|
Compound fracture - open to exterior
May result in multiple complications
|
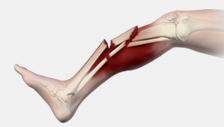 bones have multiple fractures, fragmented and open to the environment
|
A. Fracture of a healthy bone with a history of trauma - Traumatic fracture (main concern in forensic medicine) If traumatic the mechanism of causation would be direct trauma or indirect trauma.
|
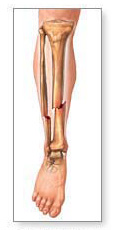
Transverse fracture fracture line is at a right angle to the long axis of the bone
|
 Oblique fracture fracture line is not at a right angle to the long axis to the bone
|
|
Green-stick fracture A crack of the bone with no disruption of the periosteum This occurs commonly among children
|
the fracture curves around the bone
|
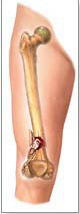 Comminuted fracture The bone is broken in to more than two parts The fracture is unstable and it is difficult to reconstruct the bone
|
Compound fracture Exposed to the environment and has a higher risk of infection related complications Seen commonly in road traffic accidents
|
|
B.
Fracture of a healthy bone with a history of repeated stress over a
along period of time
- Fatigue fracture e.g. March fracture of 2nd & 3rd metatarsals are seen in military recruits or athletes due to excessive training related stresses
C. Fracture of a bone weakened by disease ( Osteomyelitis, bone malignancy, Osteomalacia, rickets, multiple myeloma ) - Pathological fracture
|
|
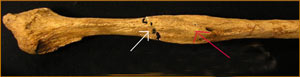 |
White arrow -
fracture Red arrow - Pathological area of the bone, weaken by malignancy
|
|
Pathological fractures on children may mimic child abuse e.g. Osteogenesis imperfecta
|
 The bow shaped femur due to osteomalacia
|
|
|
|
|

Poorly managed fracture resulting in a deformed bone |
Well managed fracture with metal plate & screws resulting in a properly healed fracture
|
|
||

Remodeling state |
|

Fracture with a callus formation |
|